Gastrointestinal Tract Diseases Overview
Gastrointestinal tract diseases are many and can be very uncomfortable and impact daily life. Understanding their common symptoms, causes, and treatments is key to managing them. With the help of the guide, individuals who experience symptoms related to structural gastrointestinal disorders, structural gi diseases, or upper GI tract. They can manage pain related digestive diseases at an early stage.
GI Stats Worldwide and in the USA
GI, and other common digestive disorders, are a big health burden worldwide. According to the World Gastroenterology Organisation (WGO), digestive diseases account for a large chunk of healthcare costs and hospitalizations globally. Moreover, GERD and IBS affect millions. As a result, liver disease and colorectal cancer are leading causes of morbidity and mortality.
Whereas, in the US, GI diseases are also common. The American Gastroenterological Association (AGA) says digestive diseases account for a large number of doctor visits and hospitalizations. Subsequently, GERD is super common. As a matter of fact, 20% of the US population is affected. Furthermore, colorectal and colon cancer also is a major public health issue. Although efforts are ongoing to promote early detection and prevention.
What is Gastrointestinal?
Gastrointestinal means the stomach (gastro) and intestines (intestinal). Additionally, it means the entire digestive tract from mouth to anus. Consequently, all the organs are involved in digestion and waste elimination.
What are 5 Common Gastrointestinal Diseases or Digestive Disorders?
The GI tract can be affected by many diseases. Here are 5 common ones:
- Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) – Abdominal pain and changed bowel habits.
- Celiac Disease – An immune reaction to eating gluten (a protein in wheat, barley, and rye).
- Crohn’s Disease – It’s a type of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) that inflames the digestive tract.
- Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD) – Acid flows back into blood vessels in the esophagus.
- Ulcerative Colitis – Another form of IBD that causes long-term inflammation and ulcers in the digestive tract.
What are the other GI Diseases?
Besides kidney diseases and the above-mentioned kidney diseases above, other major ones are:
-
Pancreatitis – Inflammation of the pancreas (acute or chronic).
-
Peptic Ulcer Disease – Sores on the stomach lining, intestine, or esophagus.
-
Liver Diseases – Hepatitis and cirrhosis that affect the liver (part of the digestive system).
- Diverticular Disease – Diverticulitis is inflammation or infection of small pouches in the intestines.
What are Gastro Intestinal Diseases and Disorders?
Gastrointestinal diseases are conditions that affect the gastrointestinal GI tract, esophagus, stomach food tube, large intestines, liver, gallbladder, and pancreas. Similarly to digestive and kidney diseases, mild to severe digestive and kidney diseases often need medical attention for management.
Whereas gastrointestinal and digestive disorders are conditions that affect the GI tract. However, these most common digestive diseases and disorders can cause abdominal pain, bloating, constipation, diarrhea, and heartburn. Functional and structural problems.
What are GI Tract Disorders?
GI Tract disorders can be classified into:
-
Inflammatory Disorders – Crohn’s and ulcerative colitis.
-
Structural Disorders – Diverticulitis and colorectal cancer.
-
Infectious Diseases – Gastroenteritis caused by viruses, bacteria, or parasites.
-
Functional Disorders – IBS where the GI tract looks normal but doesn’t work properly.
What is Gastro-Intestinal Distress and what are the Rare Intestinal Diseases?
Gastrointestinal distress is a term used to describe discomfort or pain in the digestive tract. Symptoms include nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, bloating, and changes in bowel habits. Some rare digestive disorders or other symptoms are:
-
Whipple’s Disease – A bacterial infection of the small intestine.
-
Familial Mediterranean Fever – An inherited condition that causes recurrent episodes of inflammation in the abdomen, chest, or joints.
-
Scleroderma – A rare autoimmune disease that can cause hardening and tightening of the skin and connective tissues including the GI tract.
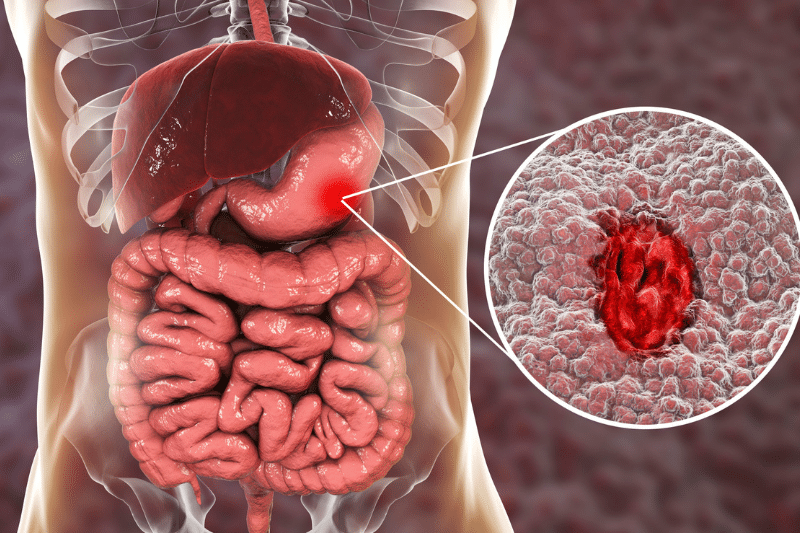
Gastrointestinal Tract Diseases – Common Gastrointestinal Disorders
What is the Most Common GI Tract Disease?
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD) is the most common GI tract disease. Not to mention, it affects millions of people worldwide, causing back pain and symptoms like heartburn, regurgitation, pain, and difficulty swallowing.
What is the Most Common Bowel Disorder?
Indeed, irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) is the most common bowel disorder. Likewise, it affects about 10-15% of the global population, according to the International Foundation for Gastrointestinal Disorders (IFFGD). IBS symptoms include stomach pain, bloating, and changes in bowel habits.
What are the Symptoms of Gastrointestinal Distress or GI Disease?
The most common GI disease is Gastroenteritis, often caused by infections, viruses, bacteria, or parasites. Symptoms of gastrointestinal distress can vary widely but commonly include the following symptoms:
-
Bloating and gas.
-
Abdominal cramping.
-
Nausea and vomiting.
-
Diarrhea or constipation.
-
Heartburn or acid reflux.
What are the Infectious Diseases of the GIT?
Infectious diseases of the gastrointestinal tract include:
-
Parasitic Infections – Including Giardia and Entamoeba histolytica.
-
Bacterial Infections – Such as Salmonella, E. coli, and Campylobacter.
-
Viral Gastroenteritis – Often called stomach flu, caused by viruses like norovirus and rotavirus.
What are Gastrointestinal Effects?
Gastrointestinal effects refer to the impact of diseases or conditions on the digestive system. Furthermore, these can include altered digestion, and nutrient absorption issues. As well as changes in your bowel movement habits. In fact, the effects of various digestive disorders and diseases can range from mild discomfort to severe, life-threatening conditions.
What is the difference between Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) and Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD)?
On one hand, IBS is a functional disorder with symptoms of abdominal pain and changes in stool habits, with no visible inflammation or damage.
Whereas, Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) includes Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis which is chronic inflammation and can cause severe damage to the GI tract.

Gastrointestinal Tract Diseases – Symptoms and Diagnosis
What are the Signs of a Serious Gastrointestinal Condition?
Serious GI conditions can present with similar symptoms:
-
Blood in stools.
-
Bloating and gas.
-
Nausea and vomiting.
-
Abdominal discomfort.
-
Chronic or severe belly pain.
-
Unintended or unexplained weight loss.
-
Diarrhea or constipation that won’t stop.
-
Jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes).
-
Heartburn or acid reflux that won’t go away.
How do I know I have issues with my intestines or Gastrointestinal Condition?
If you have ongoing digestive symptoms you may have a gastrointestinal condition. For symptoms like heartburn, abdominal cramps or stomach pain, bloating, and can’t control bowel movements or habits. If you have any of these symptoms or pain seek medical attention immediately. Also, evaluate your medical history.
What is Gastrointestinal Disturbance?
Gastrointestinal disturbance means any discomfort or irregularity in the digestive system. This can be nausea, bloating, belly pain, or changes in bowel habits. These can be caused by diet, stress, or underlying medical conditions.
What Tests are Used to Diagnose Gastrointestinal Conditions?
Several tests can diagnose gastrointestinal conditions:
-
Imaging Tests – X-rays, CT scans, MRI scans.
-
Stool Tests – To detect infections, inflammation, or other abnormalities.
-
Blood Tests – To check for signs of inflammation, infection, or celiac disease.
-
Endoscopy – A procedure using a flexible tube with a camera to see the digestive tract.
-
Colonoscopy – Same as endoscopy, the colonoscopy diagnosis colon and rectum.
Can Gastrointestinal Problems Cause Back Pain?
Yes, gastrointestinal problems can cause back pain. Pancreatitis, kidney stones, and gallbladder disease can cause referred pain in the back. Severe constipation or bloating can cause lower back pain due to pressure on the spine.
Gastrointestinal Tract Diseases – Treatments and Remedies
What is the Treatment for Gastrointestinal Disease?
Treatment for gastrointestinal diseases varies depending on the condition but some general approaches work. For example, medications are key. PPIs and H2-receptor antagonists are used for GERD to reduce stomach acid.
Antibiotics for H. pylori infections that cause peptic ulcers. Immunomodulators and biologics for inflammatory bowel diseases like Crohn’s and ulcerative colitis. To manage inflammation and maintain remission.
How Do You Treat Gastro?
Treating gastro often requires a combination of lifestyle changes and medications. Additionally, for functional disorders like IBS, dietary changes like a low-FODMAP diet can help alleviate common symptoms.
Antispasmodics and fiber supplements are also used. For severe or chronic constipation, however, laxatives or prokinetic agents may be prescribed.
How Do You Fix Gastro?
Fixing gastro is multi-faceted. First diagnostic tests like endoscopy or colonoscopy may be needed to determine the issue. Based on the results a personalized plan can be created.
This may include medication, dietary changes, and possibly surgery for structural issues. Lifestyle changes like exercise, hydration, and stress management are also part of fixing gastro.
How Do You Treat Gastrointestinal Disease?
Doctors treat the condition by addressing the underlying cause and medical history. For example, gastroenteritis caused by a virus is managed with hydration and rest.
Bacterial infections may require antibiotics, and chronic conditions like Crohn’s may require long-term medication and monitoring. Follow up with your healthcare provider to adjust treatment as needed.
What are the New Treatments for GI Diseases?
Biologic drugs that target specific parts of the immune system are new treatments for IBD. Moreover, newer drugs like vedolizumab and ustekinumab are looking good in trials. FMT is also proving to be a treatment for recurrent Clostridium difficile. These new treatments are being refined as we speak through trials.
Are there Natural Remedies for Gastrointestinal Issues?
Certainly, natural remedies can work alongside traditional treatments for digestive diseases. Evidently, probiotics are good for gut health and can help with IBS. Nevertheless, herbal supplements like peppermint oil have antispasmodic properties and can help with abdominal pain.
Again dietary approaches like ginger for nausea and chamomile for digestive discomfort are popular. But always consult with your healthcare provider before trying any natural remedy to make sure it won’t interfere with what you’re already doing.

Gastrointestinal Tract Diseases – Digestive Disorders and Issues
What is the Most Common Gut Disorder?
The most common gut disorder is Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS). Comparatively, it affects 10-15% of the population globally. Digestive diseases symptom such as bloating, and changes in your bowel movements and habits. Though, these can vary in severity and often require a combination of dietary changes, meds, and stress management to manage.
What are the GI Tract Disorders?
Each gi track disorder has its symptoms, causes, and treatment so requires individualized management. It may include:
-
Celiac Disease – An immune reaction to gluten.
-
Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) – Crohn’s and ulcerative colitis.
-
Peptic Ulcer Disease – Sores on the inner lining of the stomach or duodenum.
-
Diverticulitis – Inflammation of the pouches (diverticula) in the intestines.
-
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD) – Chronic acid reflux that damages the esophagus.
How does Stress affect the Gastrointestinal Tract?
Stress has a big impact on the gastrointestinal tract. It can worsen symptoms of IBS and GERD. Stress can affect the gut-brain axis and increase intestinal permeability, alter gut motility, and change the gut microbiota. Managing stress through mindfulness, yoga, and cognitive-behavioral therapy can help improve GI symptoms and overall digestive health.
How does Age affect the Gastrointestinal System?
Age affects the gastrointestinal system in many ways. As we age we may produce fewer digestive enzymes so digestion and nutrient absorption slow down. Motility issues like constipation become more common and the higher risk factors of developing diverticulosis and colorectal cancer increase.
In particular, older adults are more prone to medication-induced GI issues and infections. Regular screenings and a healthy diet can help mitigate some of these age-related changes.
How Does the Gastro-Intestinal System Work?
The gastrointestinal system processes food, extracts nutrients, and expels waste. For example the mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, rectum, and anus. In addition, accessory organs like the liver, pancreas, and gallbladder help in digestion by producing enzymes and bile.
Living with Gastrointestinal Digestive Disorders FAQs
What are the Long-Term Effects of Gastrointestinal Conditions?
Long-term effects of gastrointestinal conditions vary depending on the condition. Chronic digestive conditions like Crohn’s and Ulcerative Colitis can lead to strictures, fistulas, and malnutrition. Especially, if GERD left untreated can cause esophagitis and increase the risk of oesophageal cancer.
Particularly, long-term liver conditions can progress to cirrhosis and liver failure. Alternatively, managing these conditions with medical guidance can reduce the risk of long-term effects.
How can Diet and Lifestyle Changes Help with GI Conditions?
Diet and healthy lifestyle changes are key to managing GI disorders. For instance, a high-fiber diet can help with constipation, a low-FODMAP diet is effective for IBS. Further avoiding trigger foods like spicy and fatty foods can help with GERD.
Exercise regularly and gut motility and overall health will improve. Finally, stress management techniques like yoga, meditation, and sleep. They are part of a full management plan for common digestive disorders and diseases.
What are the Psychological Impacts of living with a chronic GI condition?
Living with a chronic gastrointestinal gi tract condition can have big psychological impacts. Many people experience anxiety and depression due to the unpredictability of their symptoms and the impact on their daily lives. Besides this, CBT and other forms of counseling can be helpful. Above all, support from family, friends, and healthcare professionals is key to mental well-being.
Are there any Support Groups or Resources for GI Conditions?
Yes, there are many support groups and resources for people with GI conditions. Organizations like the American Gastroenterological Association (AGA) and the Crohn & Colitis Foundation provide educational resources, support groups, and advocacy.
Also, online forums and local community groups are places to share your experience. And get support from others who are going through the same.
How to Manage Digestive Disorders and Gut Issues While Traveling?
Firstly, managing gut issues while traveling requires planning. Secondly, pack your meds and a list of dietary restrictions and emergency contacts. Thirdly, stay hydrated and try to eat regularly.
Coupled with this, choose travel-friendly, nonperishable fiber-rich supplements that fit your dietary needs. Lastly, it’s also good to research the medical facilities at your destination in case of an emergency.
Nonetheless, call us or schedule a teleconsultation if you are experiencing GI symptoms. Our experienced gastrologists would evaluate your family history to find the exact cause. Additionally, help assess the condition through physical examination and recommend treatment plan accordingly.










