Introduction to Gastric Bypass Surgery
Gastric bypass surgery is one of the most effective bariatric procedures used to help patients with severe obesity lose weight. The Roux-en-Y gastric bypass (RYGB) is often considered the gold standard of bariatric surgery procedures due to its high success rate and positive impact on obesity-related comorbidities. This surgical procedure involves creating a small gastric pouch and rerouting the small intestine, leading to reduced hunger, lower food intake, and significant weight loss. Patients can feel more confident in their treatment journey by understanding the detailed anatomy and process of gastric bypass surgery.
What is Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass?
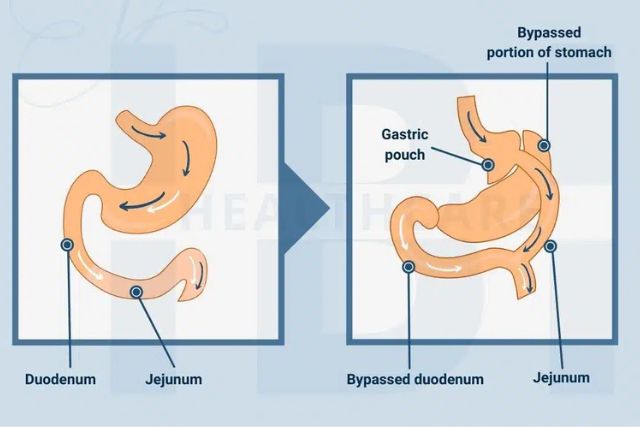
Roux-en-Y gastric bypass is a weight loss surgery that helps patients lose excess weight by altering the stomach and small intestine. The procedure creates a small gastric pouch that bypasses the gastric fundus and a portion of the small intestine, redirecting swallowed food directly into the alimentary limb. This bypass reduces the stomach’s capacity and limits the amount of food intake, contributing to significant weight loss over time. The bypassed portion of the stomach and intestines continues to perform its digestive functions, but the rerouted food flow minimizes the absorption of calories and nutrients.
The Anatomy of Gastric Bypass Surgery
In gastric bypass surgery, the surgeon creates a small gastric pouch about the size of an egg by stapling off a portion of the stomach, leaving the gastric fundus and the rest of the stomach intact but bypassed. The surgeon then connects the newly created pouch to the proximal jejunum, bypassing the duodenum and part of the small intestine. This surgical procedure reduces food intake and causes malabsorption, promoting rapid weight loss. The surgeon carefully constructs the new digestive path to optimize weight loss while minimizing the risk of complications.
Key Components of Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass Anatomy
Gastric Pouch
The newly created pouch directly receives food from the esophagus. The small gastric pouch limits the amount of food consumed at one time, resulting in less food intake and helping patients lose weight. The size of the gastric pouch is crucial, as it determines the restriction of food intake and contributes to weight loss. The small pouch holds less food, allowing patients to feel full sooner and consume fewer calories. This mechanism plays a significant role in the overall success of gastric bypass surgery.
Alimentary Limb
The alimentary or Roux limb carries swallowed food from the gastric pouch to the small intestine. This segment bypasses the duodenum, promoting malabsorption and further weight loss. The length of the alimentary limb can vary depending on the patient’s weight loss goals and specific surgical approach. By diverting food past the duodenum, the alimentary limb reduces the absorption of calories and nutrients, accelerating weight loss and minimizing the risk of weight regain.
Biliopancreatic Limb
The biliopancreatic limb carries digestive enzymes and bile from the liver and pancreas to the alimentary limb. This mixing of digestive juices occurs downstream, reducing the absorption of calories and nutrients. The biliopancreatic limb plays an essential role in the digestive process, allowing for continued digestion of fats and proteins further along the small intestine. This process ensures the body absorbs essential nutrients while minimizing overall calorie intake, contributing to sustained weight loss.
Physiological Mechanisms of Gastric Bypass
Roux-en-Y gastric bypass anatomy alters glucose metabolism, reduces hunger, and promotes weight loss. The small gastric pouch sends food directly into the small intestine, triggering hormonal changes that enhance satiety and suppress appetite. These physiological mechanisms lead to improved glucose metabolism and decreased body weight. One of the key hormones affected is ghrelin, known as the “hunger hormone,” which decreases after surgery, helping patients feel less hungry and reducing overall food intake.
Benefits of Gastric Bypass Surgery
Gastric bypass surgery helps patients lose weight, improve obesity-related comorbidities, and enhance quality of life. The procedure reduces the risk of diabetes, hypertension, and cardiovascular disease. Additionally, bariatric surgery improves body mass index (BMI) and overall metabolic health. After significant weight loss, patients often experience increased energy levels, reduced joint pain, and better mobility. This weight loss surgery enhances physical health and boosts self-confidence and mental well-being.
Bariatric Procedures: Comparing Roux-en-Y to Other Surgeries
Compared to other bariatric procedures, such as gastric banding and sleeve gastrectomy, Roux-en-Y gastric bypass has superior long-term outcomes. The procedure’s ability to induce rapid weight loss and sustain it over time makes it a preferred option for patients with morbid obesity. While gastric banding involves placing an adjustable band around the stomach to restrict food intake, Roux-en-Y gastric bypass involves a more comprehensive anatomical change resulting in restriction and malabsorption. On the other hand, sleeve gastrectomy removes a large portion of the stomach, reducing hunger but not bypassing the small intestine.
How Gastric Bypass is Performed
Gastric bypass surgery is typically performed laparoscopically under general anesthesia. This minimally invasive technique involves small incisions and specialized surgical instruments. The procedure results in a newly created pouch directly connected to the small intestine, bypassing a portion of the stomach and duodenum. Performing the surgery laparoscopically reduces the risk of complications, shortens recovery time, and minimizes scarring. The hospital discharges most patients within a few days, allowing them to return to regular activities within a few weeks.
Postoperative Care and Dietary Guidelines
After surgery, patients must follow a strict liquid diet and gradually transition to solid foods. The small pouch can only accommodate limited amounts of food, making it essential to consume nutrient-dense meals. Vitamin and mineral supplements are required to prevent nutritional deficiencies and support recovery. Patients typically start with clear liquids, progress to pureed foods, and eventually transition to soft and solid foods over several weeks. This phased approach helps the body adjust to the new digestive system and prevents complications.
Common Postoperative Complications
While Roux-en-Y gastric bypass is highly effective, it carries risks of postoperative complications. Dumping syndrome, nutritional deficiencies, and weight regain are common concerns. Patients must adhere to dietary recommendations and avoid tobacco use to minimize complications and maintain long-term weight loss. Dumping syndrome occurs when food moves too quickly from the stomach to the small intestine, causing nausea, dizziness, and diarrhea. This condition can often be managed by adjusting the diet and avoiding high-sugar foods.
Long-Term Success and Weight Maintenance
Maintaining weight loss after gastric bypass surgery requires lifestyle changes and regular follow-ups with a qualified healthcare provider. Patients must adopt healthy eating habits, engage in regular physical activity, and monitor their body weight to prevent weight regain. Ongoing support from dietitians, exercise specialists, and mental health professionals is vital in ensuring long-term success. Patients who commit to these changes are more likely to sustain weight loss and improve their overall health.
Addressing Weight Regain
Weight regain can occur if patients fail to follow postoperative guidelines. Revisional bariatric surgery may be necessary to address significant weight regain and restore the benefits of the initial procedure. Patients experiencing weight regain should consult with their surgeon to identify potential causes and develop a plan to address them. Lifestyle modifications, support groups, and counseling can help patients get back on track and maintain their weight loss goals.
Advanced Weight Loss Support at IBI Healthcare
IBI Healthcare offers a comprehensive approach to weight loss at its Advanced Weight Loss Center. With a range of bariatric surgery procedures and non-surgical weight loss solutions, patients receive personalized care to help them achieve their health goals. The center provides state-of-the-art facilities and a team of experienced specialists dedicated to long-term success. For more information, visit IBI Advanced Weight Loss Center.
Schedule an Appointment
Patients considering gastric bypass surgery or other weight loss options can schedule an appointment with IBI Healthcare to discuss their goals and explore suitable treatments. The experienced team at IBI actively guides patients through every step of their weight loss journey. To book a consultation, visit Schedule an Appointment.