With over 75% of the adult US population exhibiting higher-weight ranges, obesity has become an increasingly rampant epidemic. To combat this growing concern, physicians may suggest bariatric surgery when diet and exercise alone fail to help patients reach healthy BMI levels. Finally, what is the best procedure for Gastric Bypass vs. Duodenal Switch?
Bariatric weight loss surgery is an effective tool that can facilitate substantial weight loss for higher-weight patients.
The three standard bariatric procedures are:
- Gastric Bypass, which has been around the longest.
- Gastric Sleeve is the surgical reduction of the patient’s stomach and is step one in both the gastric bypass and duodenal switch surgeries.
- The Duodenal Switch offers the greatest weight loss potential but is also the most invasive.
The gastric sleeve has gained popularity in recent years because it is the fastest and easiest form of bariatric surgery. Today we are going to compare gastric bypass vs. duodenal switch surgeries.
The First Step In Gastric Bypass or Duodenal Switch Surgery
Surgically reducing the patient’s stomach size (often through gastric sleeve surgery), the first step of both gastric bypass and duodenal switch surgeries, we initiate these multi-step procedures.
During this first step, a surgeon cuts away and permanently removes about 75-80% of a patient’s stomach. The surgeon then brings the edges together and closes them with surgical staples. This type of bariatric technique is known as “restrictive” because it limits the amount of food a patient’s stomach can hold.
Gastric bypass and duodenal switch surgery will both promote significant weight loss but there are differences between the two that will be a factor in which procedure your bariatric surgeon may choose for your circumstances.
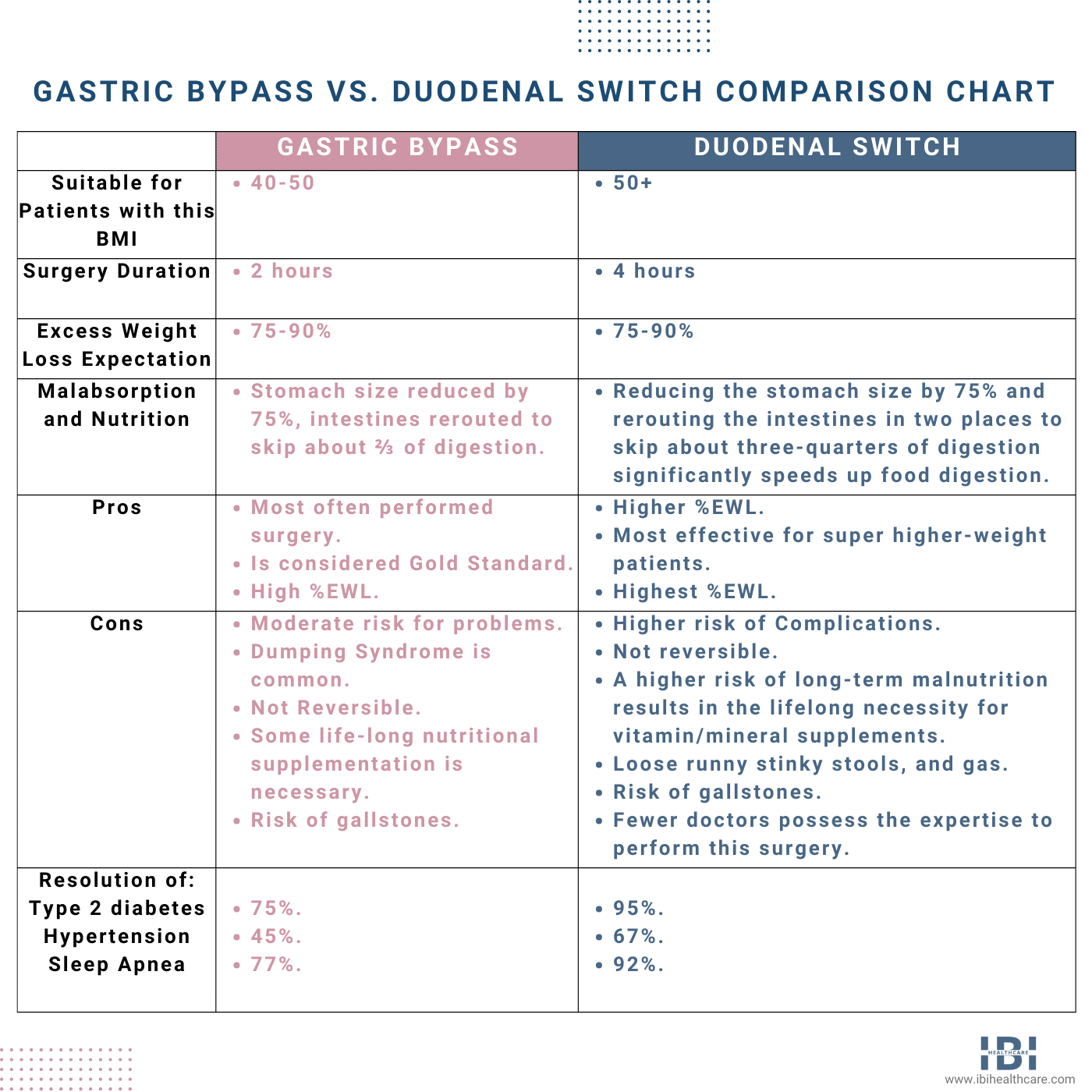
When determining between gastric bypass or duodenal switch surgery, we consider the patient’s BMI. Typically, we use gastric bypass surgery for those with a BMI in the mid-40s to 50. Moreover, if a patient’s BMI is over 50, we usually recommend duodenal switch surgery.
How Do Gastric Bypass and Duodenal Switch Differ?
An Overview Of Duodenal Switch Surgery
The medical term for this procedure is the biliopancreatic diversion with duodenal switch (BPD-DS) but is most often referred to as the duodenal switch for short.
As the least frequently performed yet most stringent, invasive, and malabsorptive bariatric surgical technique, the duodenal switch is exclusively reserved for individuals with a higher BMI and exceptional weight.
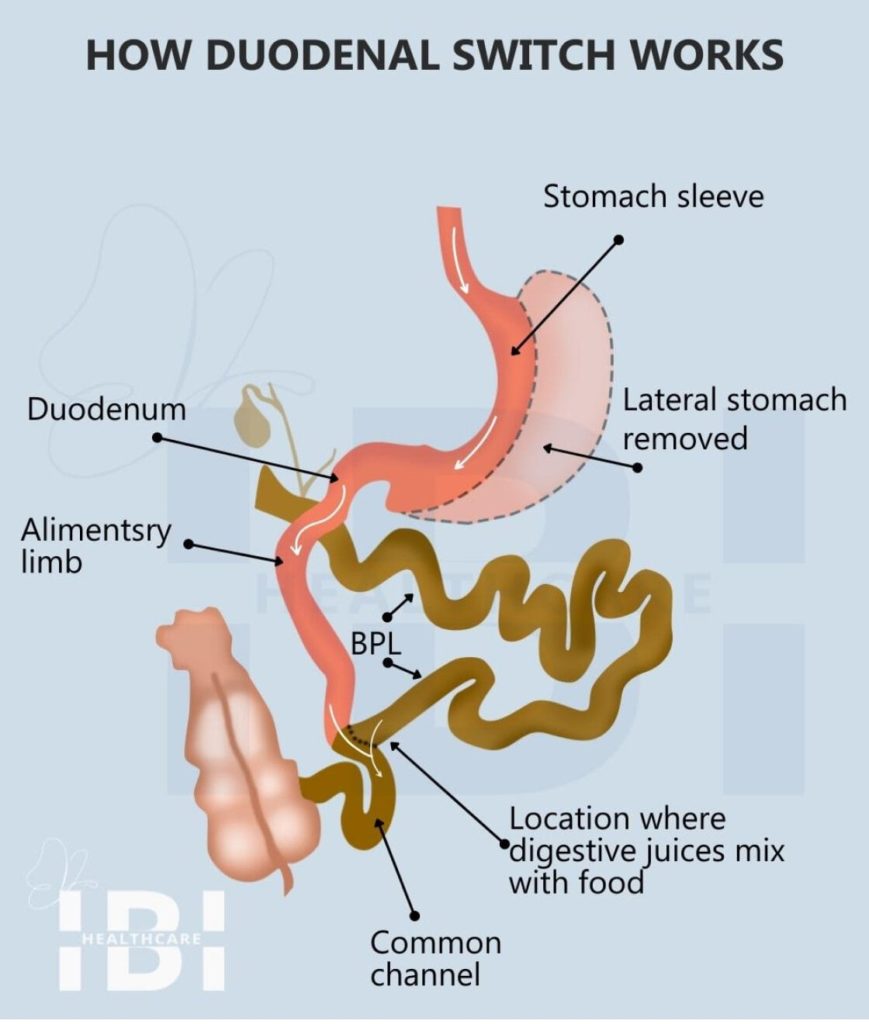
After a gastric sleeve procedure, where the medical team permanently makes the patient’s stomach smaller by surgically removing a large portion, they then proceed to the duodenal switch surgery. Next, they re-route two portions of the small intestine to bypass approximately 3⁄4 of the digestive tract. Furthermore, this malabsorptive technique limits the number of calories that can be absorbed from the ingested food.
The Duodenal switch offers both reduced stomach capacity and the bypassing of most of the normal digestive processes which work together making both metabolic and hormonal changes that promote tremendous weight loss.
An Overview of Gastric Bypass Surgery
Gastric bypass surgery (also called Roux-en-Y) has been around since the late 50s but the laparoscopic version we use today was first done in 1994. It has proven effective and is widely used by bariatric surgeons all over the world to help treat obesity.
During gastric bypass surgery, the surgeon makes the patient’s stomach smaller and alters the anatomy of the intestine to change the path of ingested food. Approximately ⅔ of the digestive process is “bypassed,” greatly reducing the number of calories absorbed by the body.
Patients ingesting smaller portions feel full faster due to the reduced stomach size, which also eliminates the majority of ghrelin, the hormone that signals hunger to the brain.
Excess Weight Loss Expectations
Calculate EWL by determining the difference between a patient’s current and goal weights. For example, for a patient whose current weight is 300 lbs. And ideal weight is 150 lbs, the EWL is 50%.
When comparing the duodenal switch vs. Roux-en-Y for excess weight loss (EWL) potential. The duodenal switch is more effective in helping patients achieve a higher percentage of EWL. Surgeons typically reserve duodenal switch surgery for higher BMI patients, due, on average, to the dramatic weight loss of 75-80% of their excess body weight. In addition, importantly, surgeons have observed the successful outcomes of this procedure.
Patients who undergo gastric bypass (Roux-en-Y) typically lose an average of 60-85% of their excess body weight which is higher than for a gastric sleeve procedure but not as much as the duodenal switch.
Nutrition and Malabsorption
Because both duodenal switch and gastric bypass surgeries involve alterations to the patient’s digestive system, these procedures put patients at a higher risk of complications due to malnutrition. The duodenal switch poses a higher risk because the alterations to the digestive system bypass a greater majority of the normal digestive process.
Gastric bypass patients experience dumping syndrome with more frequency. Compared to those who undergo the duodenal switch procedure (diarrhea and severe nausea with vomiting resulting from eating sugary or highly processed foods).
Patients who undergo gastric bypass or duodenal switch surgery must always supplement their diet with vitamins and minerals. For instance, a complete multivitamin, iron, Vitamin C, calcium, Vitamin D, and Vitamin B12. Moreover, they must eat the right foods and in the proper order.
Thus, duodenal switch surgery requires patients to take a range of supplements. It includes a multivitamin, calcium, iron, and B-complex vitamins. Alongside, fat-soluble vitamins A, D, E, and K, plus copper, zinc, and a daily probiotic.
Gastric Bypass vs. Duodenal Switch For Overall Health Improvements
Moreover, reducing weight through gastric bypass surgery and duodenal switch has proven to be remarkably effective in improving patient health. Studies show that these procedures offer drastic weight loss results. Resulting in a 75% remission rate of type 2 diabetes with gastric bypass surgery and 95% with duodenal switch. Furthermore, remission rates then continue to increase further.
Bypass and duodenal switch surgeries significantly reduce sleep apnea, joint pain, mobility issues, depression, and many severe health conditions. Patients who lose more weight reap higher percentages of improvement, regardless of surgery type. Consequently, the duodenal switch yields better results for those battling obesity-related health problems.
Gastric Bypass vs Duodenal Switch: Which Surgery is Best For You?
Both gastric bypass and duodenal switch surgeries are effective in helping patients lose a huge amount of weight. Both also prompt hormonal and metabolic changes that help reduce hunger, slow digestion, and improve or eliminate weight-related health problems.
After a consultation, the IBI Healthcare Institute can help you determine the best weight loss program for your circumstances. Moreover, you can consider bariatric surgery or explore alternative approaches for your needs.
Weigh your past loss attempts, related conditions, and goals. So we can gain an understanding of your medical history, and create a plan tailored just for you. Furthermore, today, schedule a call with us to explore your weight loss options!










